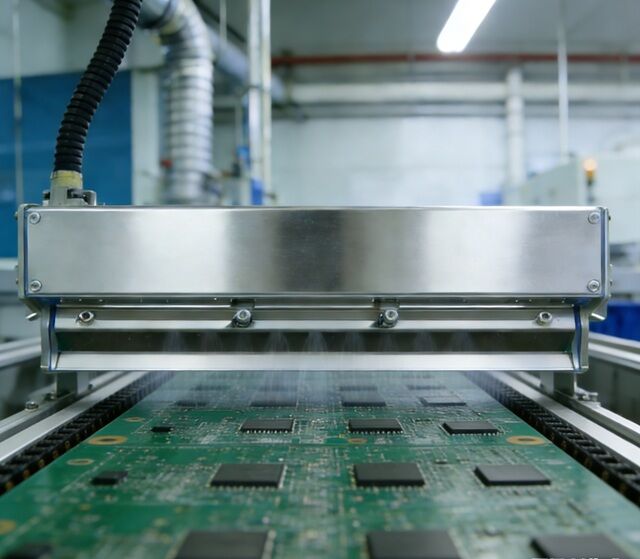
In a horizontal PCB wet process line, drying is not just a final step. It affects surface quality, yield rate, and long-term reliability of the board. After rinsing, etching, developing, or stripping, a thin layer of water stays on the copper and solder mask surfaces. If that moisture is not taken away fast and smoothly, oxidation, water marks, and chemical leftovers can happen. The result is rework, scrap, or hidden risks to reliability.
For makers running fast lines, the PCB drying process also changes cycle time and power use. Picking the right mix of air knives, sponge rollers, and airflow setup can cut drying time by several seconds per panel. It also lowers heating needs. Over thousands of panels per shift, that change is big.
Why the PCB Drying Process Matters More Than Expected
Before talking about specific parts, it is key to know what happens to water on a PCB surface.
Hidden Risks of Residual Moisture
After the last rinse, water does not sit flat. It collects along traces, holes, solder mask edges, and panel borders. On multilayer boards with tall vias, drops can stay inside holes if the airflow is weak. In work areas with room humidity over 60 percent, that moisture may not dry fast enough by itself.
Common problems tied to poor PCB drying process control include dull copper looks, white leftovers after drying, and tiny corrosion under solder mask. In bad cases, ionic dirt goes up. This can hurt insulation resistance during tests.
Impact on Throughput and Energy Use
Drying time is often a hidden slowdown. If boards leave the rinse part with too much surface water, the hot air dryer must work longer and at higher heat. That boosts power use and adds thermal stress on thin panels. By taking away most free water with machines before heating, factories can drop dryer heat by 5 to 10°C. They still get the same dryness level.
For operations that want steady quality and lower costs, fixing the machine part of the PCB drying process is a smart move. Qixingyuan supplies many components used in horizontal PCB wet lines. These include air knives and water-removal rollers made to fit different board sizes and line speeds.
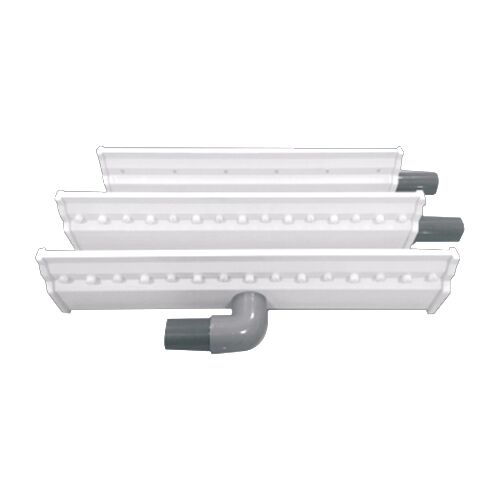
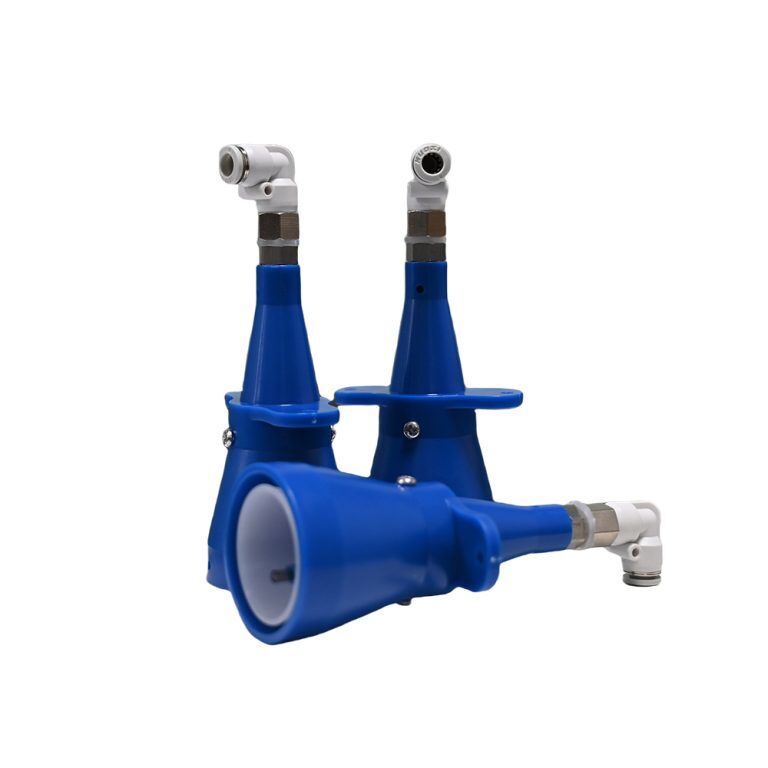
Air Knife Systems in the PCB Drying Process
Air knives are usually the first step of active drying after a rinse. Their job is not to make water evaporate. Instead, they blow it off the surface in a controlled way.
How Air Knives Remove Water
A PCB air knife makes a thin, fast sheet of air across the board surface. When set at the right angle, this airflow pushes water toward the board edge. It does not break it into fine mist. In fast lines running above 4 meters per minute, air speed and slot evenness become important. Uneven pressure leads to dry spots and wet streaks.
The angle of the air knife to the board often ranges from 30 to 60 degrees. A lower angle helps sweep water along the surface. A steeper angle can force drops out of vias. The best air knife pressure for PCB lines depends on board thickness and hole density. But many factories run between 15 and 30 kPa at the knife outlet.
Design Factors That Influence Performance
Slot width, internal airflow channel setup, and material all affect stability. Resistance to corrosion is key because air knives often work near acidic or alkaline fumes. In long runs, buildup of chemical mist can narrow the slot and mess up airflow. So, easy cleaning is useful.
When adjusted right, a PCB air knife can take away more than 80 percent of free surface water before the board hits any heated zone. This alone can cut the thermal load of the industrial PCB dryer that follows. Qixingyuan makes corrosion-resistant air knife assemblies in multiple materials and shapes. They help line builders and users match airflow performance to their specific PCB drying process needs.
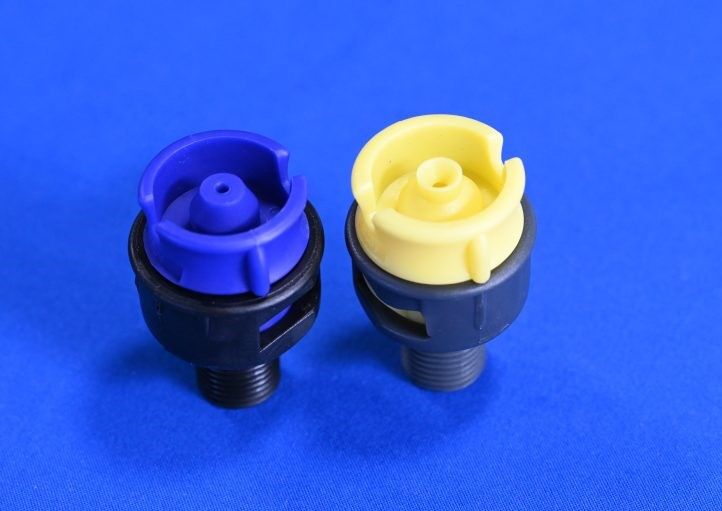
Sponge Rollers and Mechanical Water Removal
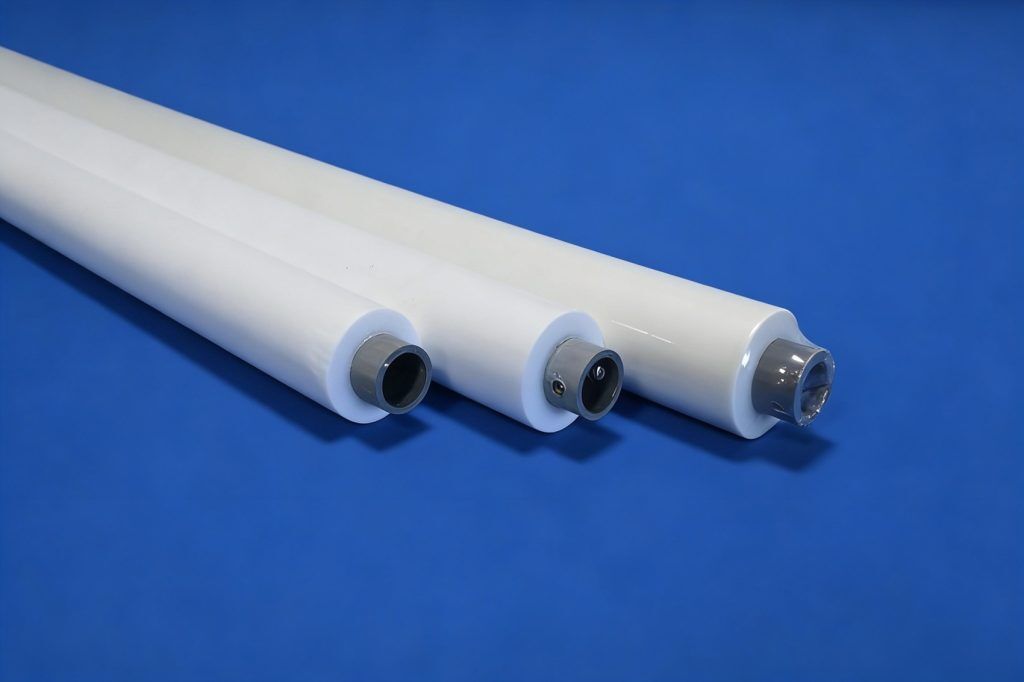

After air knives, many lines use sponge or absorbent rollers to touch the board and remove leftover drops.
Role of Sponge Rollers in Horizontal PCB Line Drying
A PCB sponge roller presses gently against the board surface while it turns. Capillary action pulls water into the sponge structure. Internal squeezing systems take out the absorbed liquid. This way is very useful for boards with dense via arrays or uneven spots where air alone cannot reach all moisture.
Different materials act in different ways in the PCB drying process. The table below shows common sponge types used in fast PCB drying equipment.
| Sponge Material | Water Absorption | Chemical Resistance | Typical Use Position | Sponge Material |
| PVA | Very high | Moderate | After rinse, before hot air | PVA |
| PU | High | Good | High speed lines, final wipe | PU |
| PP | Medium | Excellent | Harsh chemical areas | PP |
| EPDM | Medium | Very good | Acid or alkaline zones | EPDM |
In practice, a PVA sponge roller for PCB drying is often picked for its strong absorption. PU types are liked for lasting longer at higher heats.
Positioning and Line Speed Considerations
Contact pressure must be handled with care. Too much force may bend thin panels or cause marks near edges. Too little, and water stays. In lines above 5 meters per minute, two sponge stages are sometimes set up with different hardness levels. The first takes bulk water. The second polishes the surface.
Regular cleaning and squeezing work also matter. A clogged sponge loses its pull and can put dirt back. Watching this part of the PCB drying process helps keep dryness the same from the first panel to the last. Qixingyuan gives custom sponge roller solutions in various diameters and materials. They suit different board sizes, chemical settings, and transport speeds.
Combining Mechanical and Thermal Drying
Mechanical removal alone cannot get full dryness. A controlled thermal stage is still needed. But its role changes when earlier stages work well.
Hot Air and Airflow Management
In a typical industrial PCB dryer, heated air flows across the board in a tunnel section. When boards enter with little free water, the system can run at lower heat or shorter length. This cuts power draw and lowers the risk of solder mask color change.
Air spread should be even across the conveyor width. Poor airflow balance makes one side of the panel dry faster than the other. This can create slight warpage in thin materials. In modern horizontal PCB line drying setups, multiple heat zones are used. They start with moderate heat and go up slowly.
Practical Energy Savings
Factories that fixed their upstream PCB drying process often see 10 to 20 percent drop in dryer energy use. For a line running 20 hours per day, this can mean clear monthly savings. Lower heat also cuts stress on belts, bearings, and seals inside the dryer. It extends time between fixes.
By mixing well-designed air knives, absorbent rollers, and balanced hot air zones, makers can get faster drying after PCB etching and rinsing. They do this without raising costs. Qixingyuan supports this mix by supplying matching drying parts that fit into many horizontal wet process setups.
Integration, Maintenance, and Real-World Operation
Even good components need right setup and routine checks to keep the PCB drying process steady.
Line Layout and Drainage
Water taken by air knives and sponge rollers must drain well. If collection trays overflow or splash back, boards can get wet again. Proper spacing between modules stops mist from one section reaching another. In high humidity workshops, adding local exhaust near the drying stage helps keep the area steady.
Monitoring and Routine Service
Operators should check air pressure, sponge condition, and roller alignment each day. A small shift in air knife angle or worn sponge surface can lead to clear water marks on the PCB board. Keeping simple records of these checks makes it easier to find the cause of sudden quality changes.
Steady performance in the PCB drying process comes from good design and careful upkeep. Qixingyuan works with equipment builders and PCB makers to provide lasting, easy-to-fix drying components. They support long runs with fewer stops.
About Shenzhen Qixingyuan Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd.
Shenzhen Qixingyuan Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd. focuses on spare parts and accessories for PCB horizontal wet processing lines. Its product range covers air knives, sponge rollers, rubber rollers, wheels, gears, nozzles, filtration parts, and various transmission components. With experience in different chemical settings and line setups, the company helps customers who want reliable parts that fit smoothly into existing PCB equipment.
Conclusion
The PCB drying process plays a bigger role in board quality and production cost than many lines first think. By mixing effective air knife water removal, well-matched sponge rollers, and balanced hot air drying, makers can cut oxidation risk, avoid water marks, and lower energy use. Careful pick of these parts, along with regular upkeep, helps keep horizontal PCB lines running fast and steady. It also protects product reliability.